Text Analysis
By Ms. Narmadha R., Director, Centre for Data Management and Analytics
A whole lot of data is being generated all around and it is estimated that a major chunk of it is unstructured. Anything which doesn’t fit into a tabular form could be called unstructured data. Types of unstructured data include audio, video and text files. Analysis of data, in a tabular form is well known to us, as IA&AD had been using tools like MS Excel, Access and IDEA for such analysis since a long time. The recent advent of technology has enabled analysis of unstructured data too with new disciplines emerging out of analysis of images, videos and text files in the fields like bio chemistry and bio technology. This article aims to throw light on the possible utility of text analytics in SAI India.
What is Text Analytics?
Documents, Emails, online reviews, news, social media posts, notes, survey results, and other types of written information, hold insights into the subject matter. There is also a wealth of information in (voice) recorded interactions that can easily be turned into text. Similar to the way insights are drawn from numbers in structured data, insights could be drawn from words too. Text analysis is this process of deriving insights from bulk of texts (essentially words). It lets the user to uncover patterns and themes, to know what the authors are thinking about.
Text analytics tools provides valuable information from data which is not easily quantified in any other way. It turns the unstructured thoughts of authors of the text/documents into structured data that can be used by businesses and organisations.
Methodology: How is Text analysed?
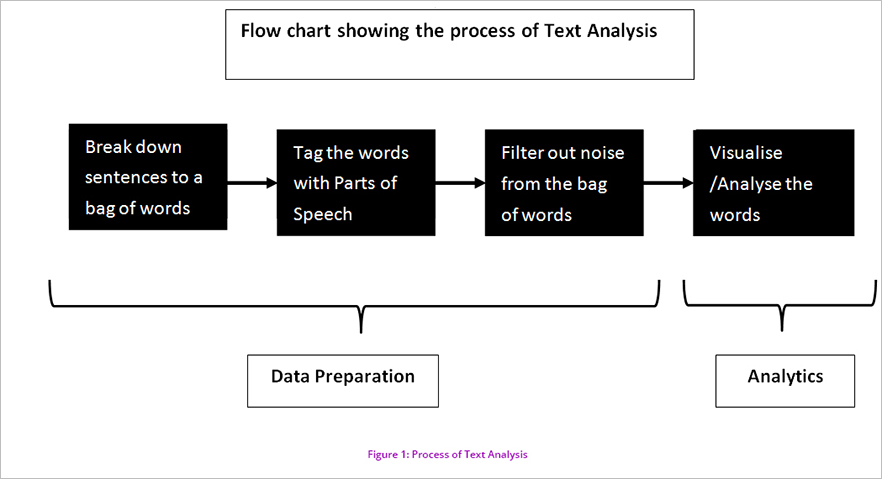
Create a Bag of Words
Text data is made up of sentences. A sentence is nothing but a string of words connected to each other. Imagine a string of pearls and what happens when the pearls are removed from the string. One is left with a string and a handful of pearls. Similarly, the first step in text processing is that every sentence is broken down into a handful of words.
Following this, the words are tagged with the respective parts of speech. For example, assume a sentence, ‘this is a good book’. There are five words in this sentence. After breaking down the sentences into five words and a symbol (.), a part of speech is tagged to each word, including the symbol, as follows: This + Pronoun; is + Conjunction, a + Conjunction, good + adjective, book + noun. This process is called enrichment. A word along with the part of speech is called as a ‘Term’. From this step onwards, an analyst will work on these ‘Terms’.
Noise Removal
Though, every dataset has varying levels of noisiness1, it is high with respect to unstructured data, especially text. Hence, the analyst works on removing the noise, that is, the unnecessary or not-so important words from this bag of words. This is essentially filtering of words, which is done on the basis of the parts of speech tagged with the words.
In our example case, say we are interested only in the adjectives, the word with parts of the speech Noun and Pronouns are removed using a conditional filter, and the word ‘good’ remains. Further, there may be many symbols, numbers, and abbreviations in the text, which are also be removed, in this process. In the example case even the full stop would be removed.
To describe in detail, imagine that the bag of terms is sieved through layers of filter, where the punctuations, symbols, numbers, foreign language words and the like get removed through each layer, so that we finally arrive at the most refined form of textual data. These words form the Analytic corpus, on which analyst runs the analytic tests.
Each of the term in this corpus is assigned weights as per the frequency of the word. Based on these weights and the part of speech, the corpus can be analysed visually or otherwise.
Text Analytic results and the utilities
An indicative list of text analytic results and utilities are given below:
Word Cloud Visualisation for Information Extraction
One of the outputs of Text analysis is a ‘Word Cloud’. It is a visual representation of the most repeated important words. The following image shows the word cloud created out of analysis of 30 Audit Inspection Reports.

A glance at the word cloud captures the imagination of the reader and gives some immediate insights into the subject matter of the IR. Also, it provokes the reader to query and drill down deeper. For example, the words ‘pay, training, Principal, staff, allowance’ suggest that the paragraphs are mostly about administrative matters of some Police Training Institute. Amongst these words, the word ‘grant’ may seem interesting to know if it is related to any grants in aid. The IR paragraph having that word may be read further to understand the context.
Analysis in a similar fashion, of the Board meeting minutes of any PSE, rules of taxation, articles/research papers on a subject, social media posts may lead to different insights.
Given below is the word cloud of ‘research papers on Infant Mortality Rate’. If one ignores the noise in the data, one can see that the words like access, income, literacy etc. catches attention. These could be the possible variables impacting Infant Mortality rate, as understood by the researchers. Such visualisation gives a first look into the subject matter without much efforts.

Analysis of Tweets on ‘Chennai Municipal Corporation’
A word cloud visualisation of tweets on a municipal corporation gives an immediate understanding of the general concerns of the citizens.

These concerns may be given a certain weightage in the risk assessment for audit planning of the unit/schemes. The relevance of tweets could not be underestimated as they are directly posted by the citizens.
Sentiment Analysis of Feedback of trainees
Sentiment analysis is a branch of text analytics where the texts posted/published by the users are analysed statistically to understand the user sentiments/opinions. For example, the social media posts related to a particular subject matter (product or a social controversy) are extracted and analysed whether most of the users have positive or negative or neutral opinions. Such insights are further used to promote the business interests.
Similar analysis of the feedback given by participants on trainings/hostel facilities in training institutes of IA&AD will help the administration in understanding the trend of feedback and areas of concern if any. Another possible area of utility is the grievances received from users with respect to entitlements like Pension/Funds/Gazetted entitlements, where the areas of concerns could be identified.
The advantage of text analytics, in these areas, is that it can provide an early warning of trouble, because it shows what the users are concerned about.
Tools
The analysis shown above has been done using Knime, an open source software. The advantage of the data analytic tools like Knime is its repeatability. The model once built can be used multiple times and can be easily distributed. It can be updated/modified as need be. Further, Knime offers the possibility of extracting textual data from the web through connectors. Tweets and google posts could be extracted through Knime. There are other tools like R, Python and SAS which can do text analytics. There are a number of sites allowing for immediate visualisation as word cloud. However, in these cases, the user text will have to be uploaded to the website servers. Care will have to be taken not to upload departmental data to these sites.
Text Analytic Applications
Utility of Text Analytics vary according to the field and area and there is no exhaustive list of applications of text analytics. Apart from Word cloud Visualisation for deriving insights, there are other applications like ‘Topic Tracking, Summarisation, Categorisation, Concept Linkage etc.,
A topic tracking system works by keeping userprofiles and, based on the documents the user views,predicts other documents of interest to the user. For example, the search words typed by viewers of SAI India website, will give insights into the viewer preferences. Summarisation could help summarizing large volumes of text on the same subject matter. Categorisation, essentially involves, identifying the types of documents into certain categories, based on the key words of the documents. Concept linkage is a valuable concept in the biomedical fields where so muchresearch has been done that it is impossible forresearchers to read all the material and make associationsto other research.
Conclusion
Text Analytics utilities have evolved uniquely in multiple branches or fields. IA&AD, as a department dealing with a lot of textual data, the utility of Text Analytics could not be overstated. The examples given above are mere illustrations, and the full scope of text analytics and its utility in ‘Audit/Accounts’ and ‘Administration’ will be an ever growing expanse.
References
- http://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/2176909/Whitepaper_The_Seven_Practice_Areas_of_Text_Analytics_Chapter_2_Excerpt.pdf
- http://text-analysis.sourceforge.net/practical-applications
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Text_mining
- http://www.expertsystem.com/10-text-mining-examples/
- https://www.slideshare.net/SethGrimes/text-analytics-solutions-applications-and-trends
- http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse634/G8present.pdf
- http://www.b-eye-network.com/view/12783
- https://thesai.org/Downloads/Volume7No11/Paper_53-Text_Mining_Techniques_Applications_and_Issues.pdf
- https://www.cio.com.au/article/575209/5-tools-techniques-text-analytics/
- http://learnpunjabi.org/pdf/gslehal-pap18.pdf
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273038150_Text_Mining_Techniques_and_its_Application
1.Noise in data simply means meaningless data. What is noisy depends on the subject matter and the objective of the analyst.
|