Data Analytics in SAI India
By Shri Deepak Mathew, Director, Center for Data Management and Analytics
In today’s wired world, literally, everything is connected and every single communication of information is recorded as ‘data’. With the generation of massive volumes of data, commonly known as Big Data and increasing availability of low cost technologies to access and process such data, ‘Analytics’ seems to be pervading all facets of life, both in the public and private sectors.
Analytics is the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data. This is done by the application of statistics (including visualisation), computer programming and operations research to quantify business performance1. Many organizations apply analytics today to the business data to describe, predict, and improve business performance.
IA&AD has also realized the potentialities of analysing data and linking multiple data in strengthening the audit process. IA&AD wishes to utilize this opportunity to make the audit process evidence based and risk analysis to be done using full potential of technology. IA&AD intends to achieve this through a systematic process with a long term vision and action plan. Centre for Data Management and Analytics (CDMA) has been formed to steer IA&AD into this new era.
Evolution
To give direction to the efforts in data analytics domain, IA&AD came out with the Big Data Management Policy in September, 2015. The policy addressed various issues confronting SAI India in Big Data arena like
- . Identification of data sources
- . Establishing data managing protocols
- . Digital Auditing, Data analytics and Visualization strategy
- . Infrastructure, capacity building and change management
While the Big Data Management Policy laid out the policy framework of SAI India in Big Data arena, a Task Force was set up to develop modalities for operationalizing the policy.Task Force in its report, submitted in May, 2016 addressed the main challenges and provided the road map for future.
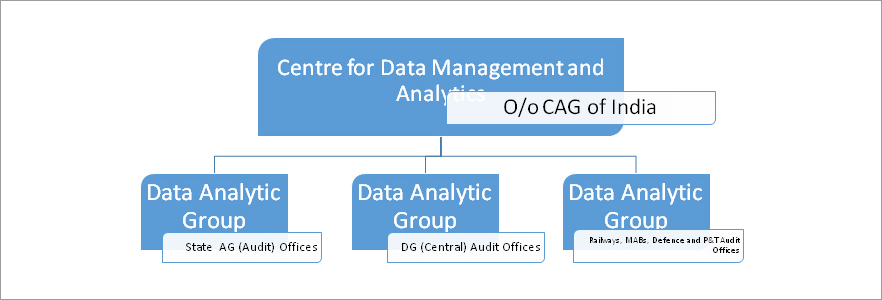
When formation of Nodal Centre on data analytics was being considered, one of the key choices confronting IA&AD was whether to create a pool of trained data analytic personnel at one Central location or to disperse the skill set in IA&AD. Considering that audit is primarily planned and executed at various field offices, it was decided to go for capacity building in all offices where domain expertise reside. Though capacity building at all the offices was a difficult proposition, it would be sustainable solution in the long run. Centre for Data Management and Analytics (CDMA) was created in June 2016 in the role of a facilitator to coordinate all the activities of data analytics in SAI India.

Centre for Data Management and Analytics
With the Big data approach and linking multiple databases, CDMA foresees a paradigm shift in the way audit is being planned in IA&AD. The idea is by using data analytics, audit teams doing substantive audit will have idea on the key risk areas in the organisation before the start of audit. This will help to identify sample for substantive audit. If transaction level data is available, sample of high risk transactions which need to be probed further can also be identified prior to start of audit. In this approach, the audit teams will be equipped with dashboards with analytical results about the organisation to be audited. Thus audit planning would become systematic depending on evidence based risk assessment.
Data analytics enables auditors to work on 100% of the transactions, instead of a sample, when the transactions are electronically recorded. With visualisation, even a non-specialist can quickly view the results graphically, easily, and have a better understanding of the audited entity. This enables auditors to improve the risk assessment process, substantive procedures and tests of controls, thereby improving audit quality. Data analytics, often, involves very simple procedures but it also includes building complex models that produce high-quality projections. CDMA envisages that data analytic efforts should not be on an ad-hoc basis. Effort should be made to make repeatable data analytic models out of the analysis done. This can be done by establishing a mechanism for periodic availability of data.
To realize the above mentioned goals, CDMA has been focusing on various activities which include:
Capacity Building
Data Analytic Groups, the nodal cell for data analytic activities has been constituted in all field audit formations of SAI India. In FY 2016-17, through 12 hands-on trainings in various parts of the country, members of these groups have been trained on latest data analytic tools and techniques. Further, advanced level training has been provided for selected officials in collaboration with premier technical and management institutions in the country.For the FY 2017-18,CDMA has drawn up plan of training more than 1000 officials at various levels in data analytics with the aim to institutionalize data analytics in SAI India.
For handling data of huge size and variety, appropriate high configuration hardware and software is being provided to field offices based on their request. CDMA is also in the process of establishing a Central Data Centre so as to assist field offices in data extraction and manipulation stages of analytics.
Pilot Projects
Around 25 pilot projects are being executed where data analytics is being used to strengthen the audit process. Data analytic activities in half of these projects have been completed. The projects are on various topics like use of data analytics in monitoring of AC-DC bills for a state government, audit of VAT, electricity department, transport department, freight operating system in railways, pension systems, social benefit systems, health and health insurance systems etc. A business intelligence model on the use of VLC data by the audit offices was also developed. The projects are diverse in that they are related to a performance audits, compliance audits or simply creating business intelligence model that would assist in planning and monitoring of audits. The approach applied in the projects has been to use data analytics at the planning stages of the audits after identifying all relatable datasets available, establishing a system for regular inflow of the data, and utilizing the same in the data analytic model developed. Thus a model created during the conduct of a performance audit may also be used for planning of compliance audits in subsequent years if the supply of data is ensured from the data sources. The model will be a compendium of data analytic insights which can be utilised by the auditors/ users of the respective offices. The learnings from these projects is being disseminated in the department.
Data Analytic Guidelines
CDMA recognizes that data analytics in Audit is an evolving area and hence the requirement of proper guidelines to move ahead systematically. CDMA is in the process of creating Guidelines on ‘Data Analytics for Audit’ touching upon the various issues involved. The guideline should be released in a few months.
Data Repository
The core of data analytics will be ‘data’ and there is need for any organisation to have robust data storage and management protocols for handling data if it has to move ahead in data analytics. SAI India is in the process of creating a data repository where data from diverse sources would be brought together and managed. CDMA has already collected data from various source like Census, Ministry of Statistics etc. as part of its effort to build Data Repository for IA&AD. CDMA is also subscribing to websites which collate data from multiple sources so as to reduce efforts in data identification and collection.
Conclusion
Data Analytics in audit and especially in public audit is an evolving domain. Though all SAIs have realized the enormous potential of data analytics in audit, the actual implementation road map is still being chartered out by many. However, it is an accepted fact that the auditor has to keep pace with the changes in the audit environment; and hence Data Analytics is to be ingrained into the audit discipline.
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analytics
|